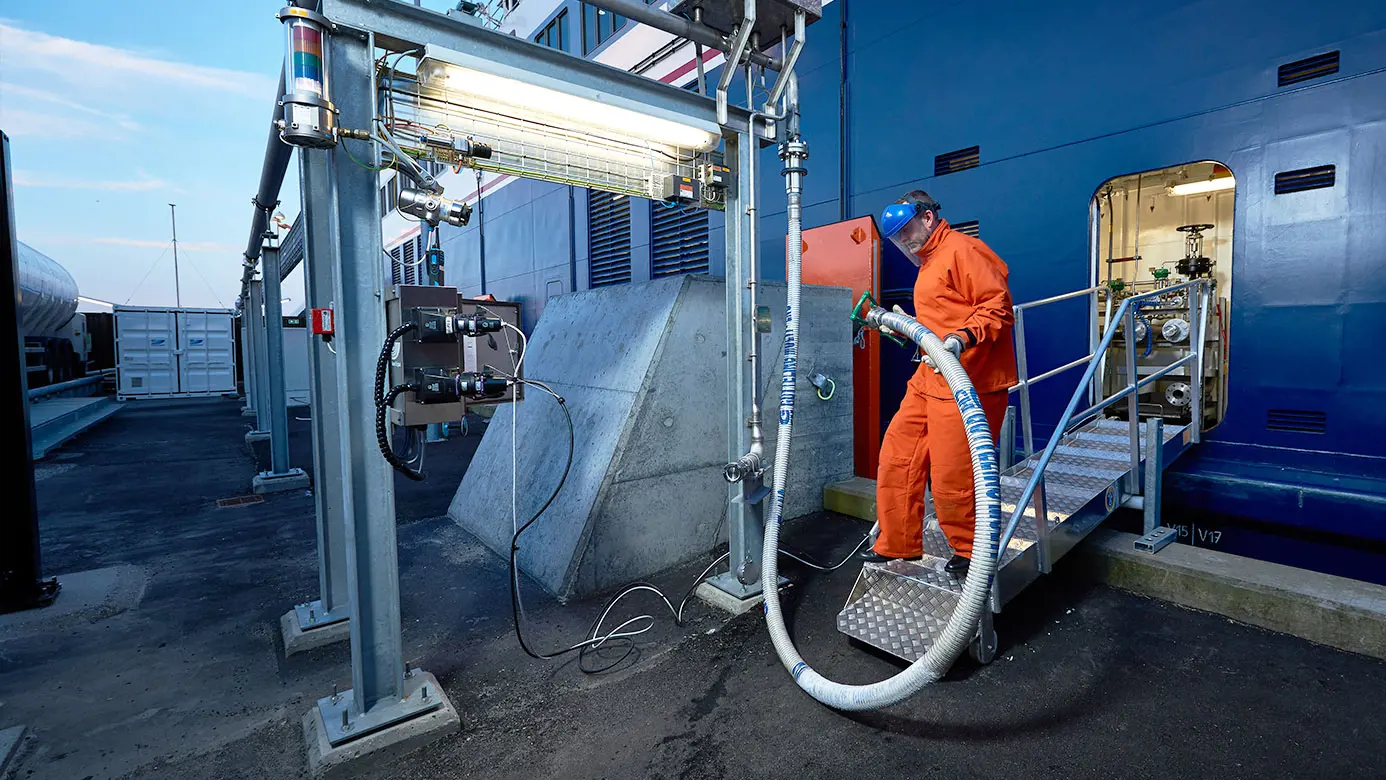
Unlike diesel and HFO, LNG does not require extensive clean-up in the unlucky situation of a spill. The natural gas simply evaporates and dissipates into the atmosphere, leaving no residue whatsoever in water or on soil to the benefit of surrounding ecosystems and water systems. As for costs, LNG is also simpler and more economical to produce than other conventional fuels. Its price is therefore more stable, enabling businesses to more accurately forecast energy costs.
With its clean burning, low CO2 content and ease of transportation, LNG is an effective energy choice for businesses that are concerned about both costs and sustainability.